Long-lost ancient Chinese silk manuscripts returned to Changsha
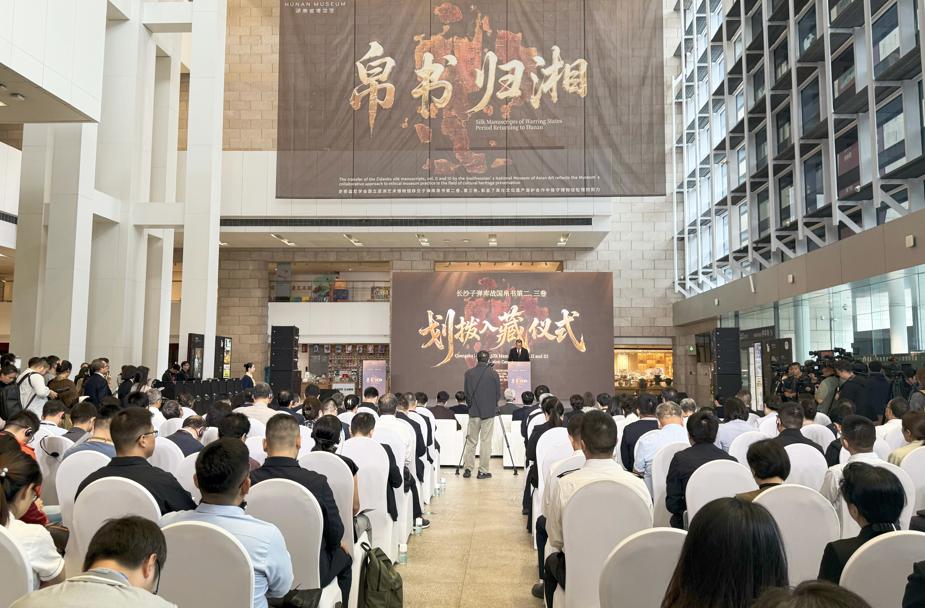


Two volumes of an ancient Chinese silk manuscript, which had been illegally taken overseas 79 years ago, have finally returned to their rightful home in Changsha, Central China's Hunan province. A repatriation ceremony was held at the Hunan Museum on Monday to mark the official return.
As the earliest Chinese silk texts discovered to date and the only known ones from the Warring States Period (475-221 BC) found in China, the manuscript was named after the Zidanku area of Changsha, where it was stolen by grave robbers in 1942. It was subsequently smuggled to the United States in 1946.
On Monday, Volumes II and III of the three-volume Zidanku Silk Manuscript, titled Wuxing Ling and Gongshou Zhan respectively, were permanently archived in the Hunan Museum.
This came after the artifacts were handed over by the Smithsonian's National Museum of Asian Art in the US and transferred to China's National Cultural Heritage Administration in May.
- Beijing launches program to foster international entrepreneurship
- China starts construction of water diversion project to quench thirst of metropolis
- China's Greater Bay Area builds world-class city cluster through connectivity, innovation
- Guangzhou forestry and fruit expo to showcase Xinjiang's specialty products
- Xi's special envoy to attend inauguration of Bolivia's president
- Tianjin's Hangu Salt Field marks 1,100th anniversary